Buy a Custom Wind Chinese or Japanese Calligraphy Wall Scroll
We have many options to create artwork with the Chinese characters / Asian symbols / Japanese Kanji for Wind on a wall scroll or portrait.
If you want to create a cool Wind wall scroll, this is the place. Below you will find a few Asian symbols that express the idea of Wind.
Switched to secondary search mode due to lack of results using primary.
These secondary results may not be very accurate. Try a different but similar meaning word or phrase for better results. Or...
Look up in my Japanese Kanji & Chinese Character Dictionary(My dictionary is a different system then the calligraphy search you just tried)
If you want a special phrase, word, title, name, or proverb, feel free to contact me, and I will translate your custom calligraphy idea for you.
1. Fix the roof before the rain; Dig the well before you are thirsty
2. Art of War: 5 Points of Analysis
5. Do not fear the task: Cooperation will lead to success
6. Dynamic
7. Feng Shui
10. Four Elements
11. Wind Wheel
12. Furinkazan
14. Hiyori
15. Hot / Heat
18. Lightning
19. Bolt of Lightning / Lightning Attack
21. One frost doesn't make winter
22. Pleasant Journey
23. Rain
24. Great Ambitions
25. Seikaze
26. Self-Discipline / Will-Power
27. Shen Long
30. Smooth Sailing
31. Storm
35. Tathata / Ultimate Nature of All Things
36. Tempest / Storm
37. Wave
38. Overcome: Regardless of the Rain and Wind
39. Regardless of the Weather, We Overcome Troubles Together
40. Wind
41. Wind and Rain
42. Wind of Change
43. Mujo no Kaze / Wind of Impermanence
44. Wind Warrior
Fix the roof before the rain; Dig the well before you are thirsty
补漏趁天晴未渴先掘井 is a Chinese proverb that literally translates as: Mend the roof while the weather is fine, [and when you are] not yet thirsty, dig the well beforehand.
In simple terms, this means: Always being prepared in advance.
See Also: Have a Walking Stick at the Ready Before You Stumble
Art of War: 5 Points of Analysis
道天地將法 is a list of five key points to analyzing your situation from the first chapter of Sun Tzu's Art of War.
This reads like a 5-part military proverb. Sun Tzu says that to sharpen your skills, you must plan. To plan well, you must know your situation. Therefore, you must consider and discuss the following:
1. Philosophy and Politics: Make sure your way or your policy is agreeable among all of your troops (and the citizens of your kingdom as well). For when your soldiers believe in you and your way, they will follow you to their deaths without hesitation and will not question your orders.
2. Heaven/Sky: Consider climate / weather. This can also mean considering whether God is smiling upon you. In the modern military, this could be waiting for clear skies so that you can have air support for an amphibious landing.
3. Ground/Earth: Consider the terrain in which the battle will take place. This includes analyzing defensible positions, and exit routes, while using varying elevations to your advantage. When you plan an ambush, you must know your terrain and the best location from which to stage that ambush. This knowledge will also help you avoid being ambushed, as you will know where the likely places in which to expect an ambush from your enemy.
4. Leadership: This applies to you as the general and your lieutenants. A leader should be smart and be able to develop good strategies. Leaders should keep their word, and if they break a promise, they should punish themselves as harshly as they would punish subordinates. Leaders should be benevolent to their troops, with almost a fatherly love for them. Leaders must have the ability to make brave and fast decisions. Leaders must have steadfast principles.
5. [Military] Methods: This can also mean laws, rules, principles, models, or systems. You must have an efficient organization in place to manage both your troops and supplies. In the modern military, this would be a combination of how your unit is organized and your SOP (Standard Operating Procedure).
Notes: This is a simplistic translation and explanation. Much more is suggested in the actual text of the Art of War (Bing Fa). It would take a lot of study to master all of these aspects. In fact, these five characters can be compared to the modern military acronyms such as BAMCIS or SMEAC.
CJK notes: I have included the Japanese and Korean pronunciations but in Chinese, Korean and Japanese, this does not make a typical phrase (with subject, verb, and object) it is a list that only someone familiar with Sun Tzu’s writings would understand.
Beauty of Nature
Ka-Chou-Fuu-Getsu
花鳥風月 is the Japanese Kanji proverb for “Beauties of Nature.”
The dictionary definition is “the traditional themes of natural beauty in Japanese aesthetics.”
The Kanji each represents an element of nature that constitutes beauty in traditional Japanese art and culture.
The Kanji breakdown:
花 = ka = flower (also pronounced “hana”)
鳥 = chou = bird (also pronounced “tori”).
風 = fuu = wind (also pronounced “kaze”).
月 = getsu = moon (also pronounced “tsuki”)
Beautiful Clear Sky
日本晴 is a Japanese Kanji title that means beautiful weather, clear and cloudless sky, or clear weather.
It's a little odd, but if you literally translated this phrase, it says, “Japanese weather,” as if that was an indication of perfect weather (maybe a little arrogant on behalf of Japan - I've experienced a monsoon there, which was unpleasant).
Do not fear the task: Cooperation will lead to success
Do not fear strong winds waves; just be sure to row in unison
不怕风浪大就怕桨不齐 is a Chinese proverb that literally translates as: Do not fear strong winds [and] high waves; what [one should] worry about whether or not you're rowing in unison.
Figuratively, this means: However difficult the task, the key to success lies in making collective efforts.
I like to translate this as “Don't sweat the details, just get together and get it done.”
Dynamic
Moving / Motion / Ever-Changing
動 is the only Chinese/Japanese/Korean word that can encompass the idea of “dynamic” into one character.
動 can also mean:
to use; to act; to move; to change; motion; stir.
In the Buddhist context, it means: Movement arises from the nature of wind which is the cause of motion.
The key point of this word is that it represents motion or always moving. Some might say “lively” or certainly the opposite of something that is stagnant or dead.
Note: In Japanese, this can also be a female given name, Yurugi.
Feng Shui
風水 is the famous technique and approach to arranging your home externally around natural features and internally to create balance and peace.
These two characters literally mean “wind water.” Obviously, the title is far more simple than the concept behind this subject.
It may enlighten you slightly to know that the character for “wind” can also mean style, custom, or manner in some contexts. This may apply somewhat to this title.
In a technical sense, this title is translated as Chinese geomancy.
Five Elements
地水火風空 is the specifically-Japanese version of the five elements.
This is a little different than the ancient or original Chinese version.
The elements are written in this order:
1. Earth / Terra / Ground
2. Water
3. Fire
4. Wind / Air
5. Sky / Emptiness / Void / Ether
Note: This set of Kanji can also be romanized as “ji sui ka fuu kuu,” “jisuikafuukuu,” or “jisuikafuku.”
These can also be written in the order 地火風水空 (chi ka sui fuu kuu). Let me know when you place your order if you want the Kanji to be in this character order.
Five Element Dojo
This is the title “5 Element Dojo” in Japanese Kanji.
Sometimes, the five elements are expressed in Japanese as 五大 (Godai) (earth, water, fire, wind, void) instead of the Chinese/Traditional 五行 (Gogyo) (wood, fire, water, earth, metal), so you might want 五大道場 instead. Let me know when ordering if that is the case.
Four Elements
Buddhist Term
地水火風 is a Buddhist term that means “earth, water, fire, wind.”
This is often just referred to as “the four elements.” There is a more common title (the five elements) that adds wood to the mix. These four elements are used in some sects of Japanese Buddhism (not so much in Chinese).
Wind Wheel
風輪 is a Chinese and Japanese Buddhist word that means Rings of Wind, or Wind Wheel.
I found this in my Buddhist dictionary while trying to figure out which “furin” people were searching for. 風輪 is one of several Japanese words that romanize as furin.
Furinkazan
military strategy
風林火山 is the battle strategy and proverb of Japanese feudal lord Takeda Shingen (1521-1573 AD).
This came from the Art of War by Chinese strategist and tactician Sun Tzu (Sunzi).
You can think of this as an abbreviation to remind officers and troops how to conduct battle.
風林火山 is a word list: Wind, Forest, Fire, Mountain.
The more expanded meaning is supposed to be...
“Swift as the wind, quiet as the forest, fierce as fire, and immovable as a mountain”
“As fast as the wind, as quiet as the forest, as daring as fire, and immovable as the mountain”
“Move as swift as the wind, stay as silent as a forest, attack as fierce as fire, undefeatable defense like a mountain”
“Move swiftly like the wind, stay silent like the forest, attack fiercely like fire, take a tactical position on the mountain”
See Also: Art of War
Godai / Five Elements
五大 is the Japanese title for the five elements.
In Japan, the five elements differ slightly from the original Chinese. Therefore, in Japanese philosophy, you have earth, water, fire, wind, and void (space).
The meaning of the first character is 5, but the second character means great or large. Some translate this as the five majors. 大 is only understood as “elements” when you have 五 in front of it.
In Buddhism, this can be short for 五大明王, or the five great and wise kings.
Hiyori
日和 is the name Hiyori in Japanese.
This can also be pronounced Biwa and can mean ideal weather when not used as a proper name.
Hot / Heat
熱 means hot in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
This can also be translated as: to warm up; to heat up; hot weather; fervent; fever; (high) temperature.
In some contexts, it can mean zeal, passion, enthusiasm, craze, or rage.
Hurricane / Typhoon
颱風/台風 is the most common way to write hurricane or typhoon in Chinese, old Korean Hanja, and Japanese Kanji. Sometimes used to refer to a big tornado as well.
The first character alone also means typhoon, but the second character means wind and acts to emphasize the meaning.

 Note: Sometimes the first character is written in the form shown to the right.
Note: Sometimes the first character is written in the form shown to the right.
Hurricane / Typhoon
颶風 is the second more common way to write hurricane or typhoon in Chinese and Japanese Kanji. Sometimes used to refer to a big tornado as well.
The first character alone also means hurricane, but the second character means wind and acts to emphasize the meaning.
Kamikaze / Divine Wind
神風 is the famous title used during WWII to describe Japanese fighter plane pilots, many of whom performed suicide attacks by flying their planes into ships and other Allied targets.
The Japanese word, Kamikaze actually means “divine wind.”
See Also: Kamikaze
Lightning
閃電 is the title for lightning in Chinese.
The first character means flash, dodge, or get out of the way. In this case, it's the “flash” meaning. Sometimes this character can be used to mean lightning by itself.
The second character means electricity.
Bolt of Lightning / Lightning Attack
Tokkan
突貫 is a Japanese word that can be translated as lightning attack, charge, or rush.
It's about a fast run or attack at the speed of lightning.
Makaze / True Wind
This Japanese word means southerly breeze or true wind.
This can also be a Japanese surname that is romanized as Makaze.
One frost doesn't make winter
一次霜凍不代表整個冬天 is a proverb that means “One frost doesn't make winter.”
The deeper meaning is that a single early sign of cold weather doesn't signify the full onset or severity of winter; it's about the gradual transition of seasons, patience, and not jumping to conclusions.
It's a reminder to stay resilient, wait for the real season to arrive, and not let one small event define the whole experience, similar to how one kind word can warm you for months.
While the origin of this proverb is murky (not originally Chinese, likely a modern adaptation of “One swallow does not a summer make”), this idea aligns with the Chinese solar terms (二十四節氣), which mark subtle shifts, like the transition from "cold dew" (寒露) to "frost falls" (霜降).
Pleasant Journey
一路順風 is a Chinese and Japanese proverb that means “to have a pleasant journey,” “sailing with the wind at your back,” or as an expression to say, “everything is going well.”
Rain
雨 is how to write “rain” in Chinese. If rain is your name or has some significance to you in your life, this is the character you want.
If your name is Varṣā or Varsha, this is how your name translates into Chinese.
Great Ambitions
Brave the wind and the waves
乘風破浪 is a Chinese proverb that represents having great ambitions.
The British might say “to plough through.” Another way to understand it is “surmount all difficulties and forge ahead courageously.”
This can also be translated as “braving the wind and waves,” “to brave the wind and the billows,” “to ride the wind and crest the waves,” or “to be ambitious and unafraid.”
Literally, it reads: “ride (like a chariot) [the] wind [and] break/cleave/cut [the] waves,” or “ride [the] wind [and] slash [through the] waves.”
乘風破浪 is a great proverb to encourage yourself or someone else not to be afraid of problems or troubles, and when you have a dream, just go for it.
There is an alternate version, 長風破浪, but 乘風破浪 is far more common.
Seikaze
静風 means quiet wind, silent wind, or serenity wind.
This can also be a given name often pronounced Seifū in Japanese and can also be pronounced Shizukaze in Japanese.
Some might also write this as 靜風 with a slight difference in the first character.
In Simplified Chinese, it's 静风.
This word is more commonly used in Japanese than Chinese, but it can be read in both languages with the same meaning.
Self-Discipline / Will-Power
自律 means self-discipline and self-control.
It is doing what you really want to do rather than being tossed around by your feelings like a leaf in the wind. You act instead of reacting. You get things done in an orderly and efficient way. With self-discipline, you take charge of yourself.
Not sure if this one works for a Japanese audience.
See Also: Discipline | Self-Control
Shen Long
神龍 or Shen Long literally means “god dragon” or “divine dragon.”
神龍 is a spiritual dragon from Chinese mythology that controls wind, storms, clouds, and rain. Historically, farmers in China avoid offending this dragon, as it could result in a drought or flooding of their fields.
Shen Long has blue/azure scales and appears on the beautiful robes of some Chinese emperors.
Sometimes romanized as Shen Lung and sometimes written as 神竜 in Japan with the pronunciation of Shinryū or Shenron. It can also be a given name in Japan.
Shidai / Sida / Mahabhuta
In Mahayana Buddhism, 四大 represents mahābhūta, the four elements of which all things are made: earth, water, fire, and wind.
This can also represent the four freedoms: speaking out freely, airing views fully, holding great debates, and writing big-character posters.
In some contexts, this can be a university or college offering four-year programs.
To others, this can represent the Tao, Heaven, Earth, and King.
Going back to the Buddhist context, these four elements “earth, water, fire, and wind,” represent 堅, 濕, 煖, 動, which are: solid, liquid, heat, and motion.
Smooth and Steady
平穩 can also be translated as calmness, quietness, or quietude and is used in Chinese and Korean.
The version shown here would be considered the ancient Japanese form. The second character has been simplified in Japan (the same simplified form is used in mainland China, except for calligraphy).
Please include special instructions with your order if you want the simplified form of that second character. Both forms can be universally read.
See Also: Smooth Sailing
Smooth Sailing
一帆風順 is just what you think it means. It suggests that you are on a trouble-free voyage through life, or literally on a sailing ship or sailboat. It is often used in China as a wish for good luck on a voyage or as you set out on a new quest or career in your life. Some may use this in place of “bon voyage.”
The literal meaning is “Once you raise your sail, you will get the wind you need, and it will take you where you want to go.” Another way to translate it is “Your sail and the wind follow your will.”
This is a great gift for a mariner, sailor, adventurer, or someone starting a new career.
Note: Can be understood in Korean Hanja but is rarely used.
See Also: Bon Voyage | Adventure | Travel
Smooth Sailing
順風満帆 means “smooth sailing” in Japanese.
The Kanji literally means “Favorable wind, full sail.”
This title can also suggest having great ambitions.
Storm
風暴 is the Chinese word for storm.
If the meaning of storm is somehow important or significant to you, these are the characters you want.
The first character means wind, and the second means violent or sudden.
Note: This would be understood in Korean Hanja, however, Koreans would generally use these characters in reverse order.
Storm / Windstorm
Best for Japanese audience
暴風 is the Japanese Kanji and old Korean Hanja word for storm (can also mean gale, tempest, typhoon, hurricane, gale, violent wind, or windstorm - especially in Korean and Chinese).
If the meaning of storm is somehow significant to you, these are the Kanji you want.
The first Kanji means violent or sudden. The second Kanji means wind.
This also means storm in Chinese but more in regards to a wind storm than a general storm. It's about the same for this word in Korean.
Strong / Powerful / Force
強 is a character that means strong, strength, force, powerful, better, stubborn, and stiff (yes, all of this in one character).
This “strong” has less to do with physical strength and more to do with having a winning attitude, or just having the ability to win at something.
Note that most of the time, this character is pronounced “qiang” but when used with the meaning of stubborn, unyielding, or stiff, it is pronounced “jiang” in Chinese.
Also, sometimes “qiang” is used in modern Chinese to describe people that do crazy things (For example: Bicycling from Beijing to Tibet alone). I sometimes can be found outside my Beijing apartment wearing nothing but shorts and a tee-shirt while eating ice cream during a snow storm, just to hear my neighbors call me “qiang.” Maybe they mean “strong” but perhaps they are using the new meaning of “crazy strong.”
強 can also be a Chinese surname that romanizes as Jiang in the mainland or Chiang if from Taiwan.
強 is a valid Korean Hanja character with the same meaning but is mostly used in compound Korean words.
強 is used in Japanese (though normally in compound words). In Japanese, it has the same meaning but in some contexts can mean “a little more than...” or “a little over [some amount].” Most Japanese would read this as tough, strength, stiff, hard, inflexible, obstinate, or stubborn.
The variant 彊 is sometimes seen in older literature.
Sunny / Clear and Bright
晴朗 is the Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja for sunny and cloudless.
This can also mean fair, serene, clear, and bright.
This usually refers to clear weather and sunny skies.
Tathata / Ultimate Nature of All Things
真如 comes from the Sanskrit and Pali word often romanized as “tathata” or “tathatā.” Originally written, “तथता.”
It's a Buddhist term often translated as “thusness” or “suchness,” but this does not explain it.
A better explanation may be “the ultimate nature of all things” or “ultimate truth.” However, this gives it too strong of a feeling. This concept is sometimes described as being in awe of the simple nature of something - like a blade of grass blowing in the wind or ripples on water. It is what it is supposed to be, these things follow their nature. Amazing in their mundane simplicity.
Every sect of Buddhism will have a slightly different flavor or explanation, so don't get fixated on one definition.
Notes: Sometimes Buddhists use the word dharmatā, a synonym to tathatā.
In Japan, this can also be the female given name Mayuki, or the surname Majo.
Tempest / Storm
暴風雨 is a Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja word meaning rainstorm, storm, or tempest.
Wave
If you like to ride a surfboard, and/or “The Way of the Wave” is your life, 波浪 could be the scroll for you.
The additional meanings contained in these characters include ripple, storm, surge, breaker, wandering, and unrestrained.
Overcome: Regardless of the Rain and Wind
風雨無阻 is a proverb that is often translated as “Go ahead as planned regardless of the weather” or, “[Overcome] despite the rain and wind.”
This is a Chinese proverb that suggests that you are willing (or should be willing) to overcome any adversity, and accomplish your task at hand.
There is a second/optional part to this phrase that suggests that you should do this together with someone (see our other 8-character version if you want the full phrase).
Regardless of the Weather, We Overcome Troubles Together
The first four characters are often translated as “Go ahead as planned regardless of the weather” or, “[Overcome] despite the rain and wind.” The last four characters can mean “Stick together” but literally means “Take the same boat [together].”
風雨無阻同舟共濟 is a Chinese proverb that suggests that you are willing (or should be willing) to overcome any adversity, and accomplish your task at hand. The second part (last four characters) is sometimes left off but this second part strongly suggests that you should overcome that adversity together.
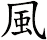
Wind
風 means wind in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
風 can also mean air, breeze, or draft. Used as a metaphor, it can mean style or manner.
See Also: Kamikaze
Wind and Rain
風雨 is wind and rain in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
This can also refer to the elements of trials and hardships (in life).
Wind of Change
風雲變幻 is a Chinese proverb that means “wind of change” or “changeable situation.”
The first character, 風, means wind, but when combined with the second character, 風雲, you have weather, winds and clouds, nature, or the elements. Colloquially, this can refer to an unstable situation or state of affairs.
The last two characters, 變幻, mean change or fluctuate.
Mujo no Kaze / Wind of Impermanence
無常の風 is an old Japanese proverb that means the wind of impermanence or the wind of change in Japanese.
This can refer to the force that ends life, like the wind scattering a flower's petals. Life is yet another impermanent existence that is fragile, blown out like a candle.
The first two characters mean uncertainty, transiency, impermanence, mutability, variable, and/or changeable.
In some Buddhist contexts, 無常 can be analogous to a spirit departing at death (with a suggestion of the impermanence of life).
The last two characters mean “of wind” or a possessive like “wind of...” but Japanese grammar will have the wind come last in the phrase.
Wind Warrior
風中戰士 is the title Wind Warrior in Chinese.
Also the name of a 2005 Hong Kong movie.
This in-stock artwork might be what you are looking for, and ships right away...

















































